Spring Cloud是一系列框架的有序集合。它利用Spring Boot的开发便利性巧妙地简化了分布式系统基础设施的开发,如服务发现注册、配置中心、智能路由、消息总线、负载均衡、断路器、数据监控等,都可以用Spring Boot的开发风格做到一键启动和部署。
Spring Cloud并没有重复制造轮子,它只是将各家公司开发的比较成熟、经得起实际考验的服务框架组合起来,通过Spring Boot风格进行再封装屏蔽掉了复杂的配置和实现原理,最终给开发者留出了一套简单易懂、易部署和易维护的分布式系统开发工具包。
服务注册与发现 eureka 服务治理组件,包括服务端的注册中心和客户端的服务发现机制;
consul 基于Hashicorp Consul的服务治理组件。
服务负载与均衡 ribbon 负载均衡的服务调用组件,具有多种负载均衡调用策略;
loadbalancer 服务负载与调用 feign 基于Ribbon和Hystrix的声明式服务调用组件;
openFeign 基于Ribbon和Hystrix的声明式服务调用组件,可以动态创建基于Spring MVC注解的接口实现用于服务调用,在Spring Cloud 2.0中已经取代Feign成为了一等公民。
服务熔断与降级 hystrix 服务容错组件,实现了断路器模式,为依赖服务的出错和延迟提供了容错能力;
resilience4j 服务网关 zuul API网关组件,对请求提供路由及过滤功能。
zuul2 getway API网关组件,对请求提供路由及过滤功能。
服务分布式配置 springcloud config 集中配置管理工具,分布式系统中统一的外部配置管理,默认使用Git来存储配置,可以支持客户端配置的刷新及加密、解密操作。
Nacos 总线 Spring Cloud Bus 用于传播集群状态变化的消息总线,使用轻量级消息代理链接分布式系统中的节点,可以用来动态刷新集群中的服务配置。
springcloudAlibaba Nacos Nacos 是一个开源的分布式系统服务发现、配置管理和服务管理平台。它主要包含以下功能:
服务发现与注册:Nacos 可以管理服务的注册和发现,支持 DNS 和 HTTP/RESTful 方式。
服务发现与注册 Nacos 实现服务发现和注册的核心代码位于 nacos/naming 目录下,包括以下文件:
naming-common/src/main/java/com/alibaba/nacos/api/naming: 定义了服务发现和注册的 API 接口和数据模型。
naming-core/src/main/java/com/alibaba/nacos/naming: 实现了服务发现和注册的核心逻辑。
naming-impl/src/main/java/com/alibaba/nacos/naming: 实现了服务发现和注册的具体实现。
下面简单介绍一下 Nacos 的服务发现和注册的实现流程。
服务注册流程 服务提供者向 Nacos 注册服务时,会调用 NamingService.registerInstance() 方法,该方法会做以下几件事情:
将服务实例的元数据封装为 Instance 对象,包括服务名、IP、端口号、健康状态、元数据等。
将 Instance 对象转换为 InstanceEntity 对象,包含了实例 ID 和实例元数据的 JSON 字符串。
将 InstanceEntity 对象存储到 Nacos 中,可以存储到内存中或者持久化到磁盘中。
服务发现流程 服务消费者向 Nacos 发现服务时,会调用 NamingService.getAllInstances() 或 NamingService.selectInstances() 方法,该方法会做以下几件事情:
从 Nacos 中获取服务实例的元数据,包括服务名、IP、端口号、健康状态、元数据等。
将元数据封装为 Instance 对象,存储到本地缓存中。
根据负载均衡算法选择一个服务实例处理请求,可以选择轮询、随机、权重等算法。
服务发现和注册的核心逻辑在 naming-core 目录下的 com.alibaba.nacos.naming 包中实现,主要包括以下类:
com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.InstancesManager: 维护服务实例的元数据和状态信息。
com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.Cluster: 维护一个服务的所有实例信息和负载均衡策略。
com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.InstanceOperator: 实现了服务实例的注册、注销和更新操作。
com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.DomainsManager: 维护多个服务的信息,包括服务名、集群名、命名空间等。
服务发现和注册的具体实现在 naming-impl 目录下的 com.alibaba.nacos.naming 包中,主要包括以下类:
com.alibaba.nacos.naming.push.PushService: 实现了服务实例的推送功能。
com.alibaba.nacos.naming.healthcheck.HealthCheckProcessor: 实现了服务实例的健康检查功能。
com.alibaba.nacos.naming.misc.GlobalConfig: 存储了一些全局配置,例如默认权重值、心跳间隔
配置动态刷新 从远端服务器获取变更数据的主要模式有两种:推(push)和拉(pull)。Push 模式简单来说就是服务端主动将数据变更信息推送给客户端,这种模式优点是时效性好,服务端数据发生变更可以立马通知到客户端,但这种模式需要服务端维持与客户端的心跳连接,会增加服务端实现的复杂度,服务端也需要占用更多的资源来维持与客户端的连接。
而 Pull 模式则是客户端主动去服务器请求数据,例如,每间隔10ms就向服务端发起请求获取数据。显而易见pull模式存在时效性问题。请求的间隔也不太好设置,间隔太短,对服务器请求压力过大。间隔时间过长,那么必然会造成时效性很差。而且如果配置长时间不更新,并且存在大量的客户端就会产生大量无效的pull请求。
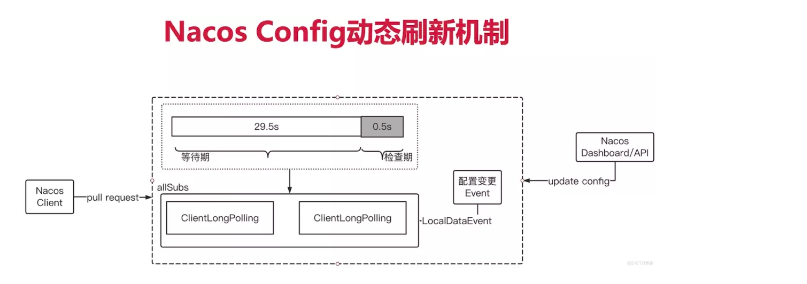
Nacos 没有采用上述的两种模式,而是采用了长轮询方式结合了推和拉的优点:
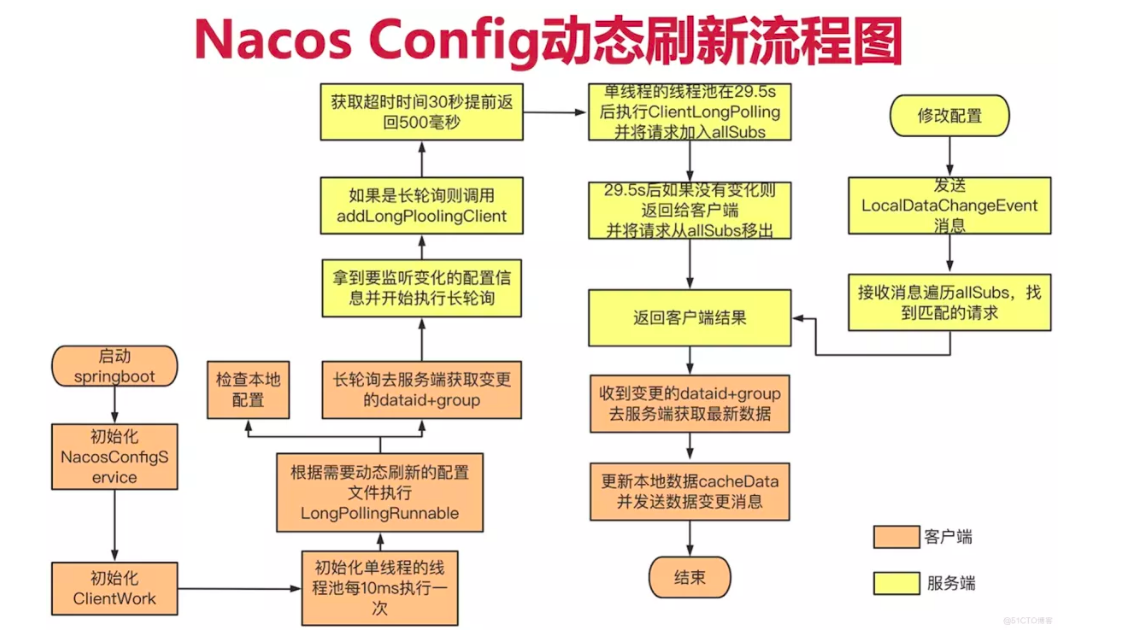
长轮询也是轮询,因此 Nacos 客户端会默认每10ms向服务端发起请求,当客户端请求服务端时会在请求头上携带长轮询的超时时间,默认是30s。而服务端接收到该请求时会hang住请求,为了防止客户端超时会在请求头携带的超时时间上减去500ms,因此默认会hang住请求29.5s。在这期间如果服务端发生了配置变更会产生相应的事件,监听到该事件后,会响应对应的客户端。这样一来客户端不会频繁发起轮询请求,而服务端也不需要维持与客户端的心跳,兼备了时效性和复杂度。
1.4版本nacos使用Http短连接+长轮询的方式,客户端发起http请求,服务端hold住请求,当配置变更时响应客户端,超时时间30s。
Nacos Config 长轮询源码剖析 首先,打开 com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.NacosConfigBootstrapConfiguration 这个类,从类名也可以看出该类是Nacos Config的启动配置类,是Nacos Config自动装配的入口。在该类中的 nacosConfigManager 方法实例化了一个 NacosConfigManager 对象,并注册到容器中:
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public NacosConfigManager nacosConfigManager ( NacosConfigProperties nacosConfigProperties) { return new NacosConfigManager (nacosConfigProperties); }
在 NacosConfigManager 的构造器中调用了 createConfigService 方法,这是一个静态方法用来创建 ConfigService 对象的单例。
static ConfigService createConfigService ( NacosConfigProperties nacosConfigProperties) { if (Objects.isNull(service)) { synchronized (NacosConfigManager.class) { try { if (Objects.isNull(service)) { service = NacosFactory.createConfigService( nacosConfigProperties.assembleConfigServiceProperties()); } } catch (NacosException e) { log.error(e.getMessage()); throw new NacosConnectionFailureException ( nacosConfigProperties.getServerAddr(), e.getMessage(), e); } } } return service; }
ConfigService 的具体实现是 NacosConfigService,在该类的构造器中主要初始化了 HttpAgent 和 ClientWorker 对象。ClientWorker 的构造器中则初始化了几个线程池:
public ClientWorker (final HttpAgent agent, final ConfigFilterChainManager configFilterChainManager, final Properties properties) { this .agent = agent; this .configFilterChainManager = configFilterChainManager; init(properties); this .executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1 , new ThreadFactory () { @Override public Thread newThread (Runnable r) { Thread t = new Thread (r); t.setName("com.alibaba.nacos.client.Worker." + agent.getName()); t.setDaemon(true ); return t; } }); this .executorService = Executors .newScheduledThreadPool(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(), new ThreadFactory () { @Override public Thread newThread (Runnable r) { Thread t = new Thread (r); t.setName("com.alibaba.nacos.client.Worker.longPolling." + agent.getName()); t.setDaemon(true ); return t; } }); this .executor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable () { @Override public void run () { try { checkConfigInfo(); } catch (Throwable e) { LOGGER.error("[" + agent.getName() + "] [sub-check] rotate check error" , e); } } }, 1L , 10L , TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } private void init (Properties properties) { timeout = Math.max(ConvertUtils.toInt(properties.getProperty(PropertyKeyConst.CONFIG_LONG_POLL_TIMEOUT), Constants.CONFIG_LONG_POLL_TIMEOUT), Constants.MIN_CONFIG_LONG_POLL_TIMEOUT); taskPenaltyTime = ConvertUtils .toInt(properties.getProperty(PropertyKeyConst.CONFIG_RETRY_TIME), Constants.CONFIG_RETRY_TIME); this .enableRemoteSyncConfig = Boolean .parseBoolean(properties.getProperty(PropertyKeyConst.ENABLE_REMOTE_SYNC_CONFIG)); } public void checkConfigInfo () { int listenerSize = cacheMap.size(); int longingTaskCount = (int ) Math.ceil(listenerSize / ParamUtil.getPerTaskConfigSize()); if (longingTaskCount > currentLongingTaskCount) { for (int i = (int ) currentLongingTaskCount; i < longingTaskCount; i++) { executorService.execute(new LongPollingRunnable (i)); } currentLongingTaskCount = longingTaskCount; } }
LongPollingRunnable 类主要用于检查本地配置,以及长轮询地去服务端获取变更配置的 dataid 和 group,其代码位于 com.alibaba.nacos.client.config.impl.ClientWorker 类,代码如下:
class LongPollingRunnable implements Runnable { private final int taskId; public LongPollingRunnable (int taskId) { this .taskId = taskId; } @Override public void run () { List<CacheData> cacheDatas = new ArrayList <CacheData>(); List<String> inInitializingCacheList = new ArrayList <String>(); try { for (CacheData cacheData : cacheMap.values()) { if (cacheData.getTaskId() == taskId) { cacheDatas.add(cacheData); try { checkLocalConfig(cacheData); if (cacheData.isUseLocalConfigInfo()) { cacheData.checkListenerMd5(); } } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error("get local config info error" , e); } } } List<String> changedGroupKeys = checkUpdateDataIds(cacheDatas, inInitializingCacheList); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(changedGroupKeys)) { LOGGER.info("get changedGroupKeys:" + changedGroupKeys); } for (String groupKey : changedGroupKeys) { String[] key = GroupKey.parseKey(groupKey); String dataId = key[0 ]; String group = key[1 ]; String tenant = null ; if (key.length == 3 ) { tenant = key[2 ]; } try { String[] ct = getServerConfig(dataId, group, tenant, 3000L ); CacheData cache = cacheMap.get(GroupKey.getKeyTenant(dataId, group, tenant)); cache.setContent(ct[0 ]); if (null != ct[1 ]) { cache.setType(ct[1 ]); } LOGGER.info("[{}] [data-received] dataId={}, group={}, tenant={}, md5={}, content={}, type={}" , agent.getName(), dataId, group, tenant, cache.getMd5(), ContentUtils.truncateContent(ct[0 ]), ct[1 ]); } catch (NacosException ioe) { String message = String .format("[%s] [get-update] get changed config exception. dataId=%s, group=%s, tenant=%s" , agent.getName(), dataId, group, tenant); LOGGER.error(message, ioe); } } for (CacheData cacheData : cacheDatas) { if (!cacheData.isInitializing() || inInitializingCacheList .contains(GroupKey.getKeyTenant(cacheData.dataId, cacheData.group, cacheData.tenant))) { cacheData.checkListenerMd5(); cacheData.setInitializing(false ); } } inInitializingCacheList.clear(); executorService.execute(this ); } catch (Throwable e) { LOGGER.error("longPolling error : " , e); executorService.schedule(this , taskPenaltyTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } } }
上面有个 checkUpdateDataIds 方法,用于获取发生变更了的配置文件的dataId列表,它同样位于 ClientWorker 内。如下:
List<String> checkUpdateDataIds (List<CacheData> cacheDatas, List<String> inInitializingCacheList) throws Exception { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); for (CacheData cacheData : cacheDatas) { if (!cacheData.isUseLocalConfigInfo()) { sb.append(cacheData.dataId).append(WORD_SEPARATOR); sb.append(cacheData.group).append(WORD_SEPARATOR); if (StringUtils.isBlank(cacheData.tenant)) { sb.append(cacheData.getMd5()).append(LINE_SEPARATOR); } else { sb.append(cacheData.getMd5()).append(WORD_SEPARATOR); sb.append(cacheData.getTenant()).append(LINE_SEPARATOR); } if (cacheData.isInitializing()) { inInitializingCacheList .add(GroupKey.getKeyTenant(cacheData.dataId, cacheData.group, cacheData.tenant)); } } } boolean isInitializingCacheList = !inInitializingCacheList.isEmpty(); return checkUpdateConfigStr(sb.toString(), isInitializingCacheList); } List<String> checkUpdateConfigStr (String probeUpdateString, boolean isInitializingCacheList) throws Exception { Map<String, String> params = new HashMap <String, String>(2 ); params.put(Constants.PROBE_MODIFY_REQUEST, probeUpdateString); Map<String, String> headers = new HashMap <String, String>(2 ); headers.put("Long-Pulling-Timeout" , "" + timeout); if (isInitializingCacheList) { headers.put("Long-Pulling-Timeout-No-Hangup" , "true" ); } if (StringUtils.isBlank(probeUpdateString)) { return Collections.emptyList(); } try { long readTimeoutMs = timeout + (long ) Math.round(timeout >> 1 ); HttpRestResult<String> result = agent .httpPost(Constants.CONFIG_CONTROLLER_PATH + "/listener" , headers, params, agent.getEncode(), readTimeoutMs); if (result.ok()) { setHealthServer(true ); return parseUpdateDataIdResponse(result.getData()); } else { setHealthServer(false ); LOGGER.error("[{}] [check-update] get changed dataId error, code: {}" , agent.getName(), result.getCode()); } } catch (Exception e) { setHealthServer(false ); LOGGER.error("[" + agent.getName() + "] [check-update] get changed dataId exception" , e); throw e; } return Collections.emptyList(); }
客户端对 listener 接口的请求会进入到服务端的 com.alibaba.nacos.config.server.controller.ConfigController#listener 方法进行处理,该方法主要是调用了 com.alibaba.nacos.config.server.controller.ConfigServletInner#doPollingConfig 方法。代码如下:
public String doPollingConfig (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Map<String, String> clientMd5Map, int probeRequestSize) throws IOException, ServletException { if (LongPollingService.isSupportLongPolling(request)) { longPollingService.addLongPollingClient(request, response, clientMd5Map, probeRequestSize); return HttpServletResponse.SC_OK + "" ; } List<String> changedGroups = MD5Util.compareMd5(request, response, clientMd5Map); String oldResult = MD5Util.compareMd5OldResult(changedGroups); String newResult = MD5Util.compareMd5ResultString(changedGroups); String version = request.getHeader(Constants.CLIENT_VERSION_HEADER); if (version == null ) { version = "2.0.0" ; } int versionNum = Protocol.getVersionNumber(version); if (versionNum < START_LONGPOLLING_VERSION_NUM) { response.addHeader(Constants.PROBE_MODIFY_RESPONSE, oldResult); response.addHeader(Constants.PROBE_MODIFY_RESPONSE_NEW, newResult); } else { request.setAttribute("content" , newResult); } response.setHeader("Pragma" , "no-cache" ); response.setDateHeader("Expires" , 0 ); response.setHeader("Cache-Control" , "no-cache,no-store" ); response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK); return HttpServletResponse.SC_OK + "" ; }
我们主要关注上面的 com.alibaba.nacos.config.server.service.LongPollingService#addLongPollingClient 长轮询流程的方法。代码如下:
public void addLongPollingClient (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse rsp, Map<String, String> clientMd5Map, int probeRequestSize) { String str = req.getHeader(LongPollingService.LONG_POLLING_HEADER); String noHangUpFlag = req.getHeader(LongPollingService.LONG_POLLING_NO_HANG_UP_HEADER); String appName = req.getHeader(RequestUtil.CLIENT_APPNAME_HEADER); String tag = req.getHeader("Vipserver-Tag" ); int delayTime = SwitchService.getSwitchInteger(SwitchService.FIXED_DELAY_TIME, 500 ); long timeout = Math.max(10000 , Long.parseLong(str) - delayTime); if (isFixedPolling()) { timeout = Math.max(10000 , getFixedPollingInterval()); } else { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); List<String> changedGroups = MD5Util.compareMd5(req, rsp, clientMd5Map); if (changedGroups.size() > 0 ) { generateResponse(req, rsp, changedGroups); LogUtil.clientLog.info("{}|{}|{}|{}|{}|{}|{}" , System.currentTimeMillis() - start, "instant" , RequestUtil.getRemoteIp(req), "polling" , clientMd5Map.size(), probeRequestSize, changedGroups.size()); return ; } else if (noHangUpFlag != null && noHangUpFlag.equalsIgnoreCase(TRUE_STR)) { LogUtil.clientLog.info("{}|{}|{}|{}|{}|{}|{}" , System.currentTimeMillis() - start, "nohangup" , RequestUtil.getRemoteIp(req), "polling" , clientMd5Map.size(), probeRequestSize, changedGroups.size()); return ; } } String ip = RequestUtil.getRemoteIp(req); final AsyncContext asyncContext = req.startAsync(); asyncContext.setTimeout(0L ); scheduler.execute( new ClientLongPolling (asyncContext, clientMd5Map, ip, probeRequestSize, timeout, appName, tag)); }
而 LongPollingService 实现了 AbstractEventListener,也就是说能接收事件通知,在其 com.alibaba.nacos.config.server.service.LongPollingService#onEvent 方法中可以看到,它关注的是 LocalDataChangeEvent 事件:
@Override public void onEvent (Event event) { if (isFixedPolling()) { } else { if (event instanceof LocalDataChangeEvent) { LocalDataChangeEvent evt = (LocalDataChangeEvent)event; scheduler.execute(new DataChangeTask (evt.groupKey, evt.isBeta, evt.betaIps)); } } }
在nacos上修改配置后就会产生 LocalDataChangeEvent 事件,此时 LongPollingService 也就能监听到,当收到该事件时就会遍历 allSubs,找到匹配的请求并将 groupKey 返回给客户端。具体代码在 DataChangeTask 中:
class DataChangeTask implements Runnable { @Override public void run () { try { ConfigService.getContentBetaMd5(groupKey); for (Iterator<ClientLongPolling> iter = allSubs.iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) { ClientLongPolling clientSub = iter.next(); if (clientSub.clientMd5Map.containsKey(groupKey)) { if (isBeta && !betaIps.contains(clientSub.ip)) { continue ; } if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(tag) && !tag.equals(clientSub.tag)) { continue ; } getRetainIps().put(clientSub.ip, System.currentTimeMillis()); iter.remove(); LogUtil.clientLog.info("{}|{}|{}|{}|{}|{}|{}" , (System.currentTimeMillis() - changeTime), "in-advance" , RequestUtil.getRemoteIp((HttpServletRequest)clientSub.asyncContext.getRequest()), "polling" , clientSub.clientMd5Map.size(), clientSub.probeRequestSize, groupKey); clientSub.sendResponse(Arrays.asList(groupKey)); } } } catch (Throwable t) { LogUtil.defaultLog.error("data change error:" + t.getMessage(), t.getCause()); } } DataChangeTask(String groupKey) { this (groupKey, false , null ); } DataChangeTask(String groupKey, boolean isBeta, List<String> betaIps) { this (groupKey, isBeta, betaIps, null ); } DataChangeTask(String groupKey, boolean isBeta, List<String> betaIps, String tag) { this .groupKey = groupKey; this .isBeta = isBeta; this .betaIps = betaIps; this .tag = tag; } final String groupKey; final long changeTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); final boolean isBeta; final List<String> betaIps; final String tag; }
当客户端收到变更的dataid+group后,就会去服务端获取最新的配置数据,并更新本地数据 cacheData,然后发送数据变更事件,整个流程结束。
获取服务端最新配置数据的方法:com.alibaba.nacos.client.config.impl.ClientWorker#getServerConfig
发送数据变更事件的方法:com.alibaba.nacos.client.config.impl.CacheData#checkListenerMd5
Sentienl Sentinel是阿里巴巴开源的一款流量控制和熔断降级框架,主要用于微服务架构中服务的流量控制和熔断降级。其限流实现原理主要分为两个部分:
统计信息收集
Sentinel会在运行过程中对服务的各种统计信息进行收集,包括请求的响应时间、请求通过的QPS(每秒查询率)、线程池队列大小等指标。这些指标通过定义的规则进行分析,判断当前请求是否超过了设定的阈值。
阈值判断
Sentinel根据收集到的统计信息,通过定义的规则对请求进行判断。规则中包括以下几个要素:
资源名:对哪个资源进行限流
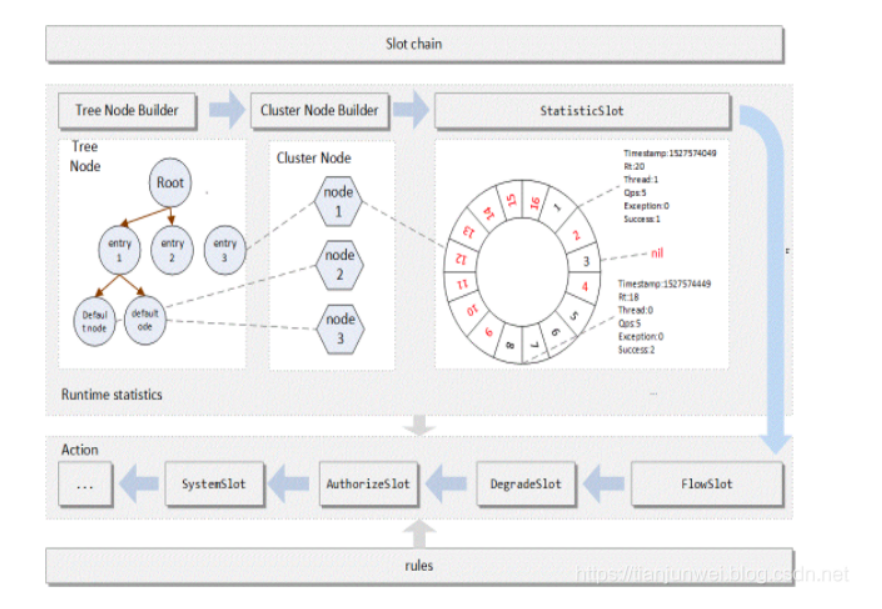
工作原理 Slot 插槽 在 Sentinel 里面,所有的资源都对应一个资源名称(resourceName),每次资源调用都会创建一个 Entry 对象。Entry 可以通过对主流框架的适配自动创建,也可以通过注解的方式或调用 SphU API 显式创建。Entry 创建的时候,同时也会创建一系列功能插槽(slot chain),这些插槽有不同的职责,例如:
NodeSelectorSlot 负责收集资源的路径,并将这些资源的调用路径,以树状结构存储起来,用于根据调用路径来限流降级;
ClusterBuilderSlot 则用于存储资源的统计信息以及调用者信息,例如该资源的 RT, QPS, thread count 等等,这些信息将用作为多维度限流,降级的依据;
StatisticSlot 则用于记录、统计不同纬度的 runtime 指标监控信息;
FlowSlot 则用于根据预设的限流规则以及前面 slot 统计的状态,来进行流量控制;
AuthoritySlot 则根据配置的黑白名单和调用来源信息,来做黑白名单控制;
DegradeSlot 则通过统计信息以及预设的规则,来做熔断降级;
SystemSlot 则通过系统的状态,例如 load1 等,来控制总的入口流量;
Sentinel 提供了插槽接口 ProcessorSlot,其中提供了方法 enrty 处理进入请求 和 exit 处理请求结束操作
public interface ProcessorSlot <T> { void entry (Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, T param, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable; void fireEntry (Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object obj, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable; void exit (Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) ; void fireExit (Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) ; }
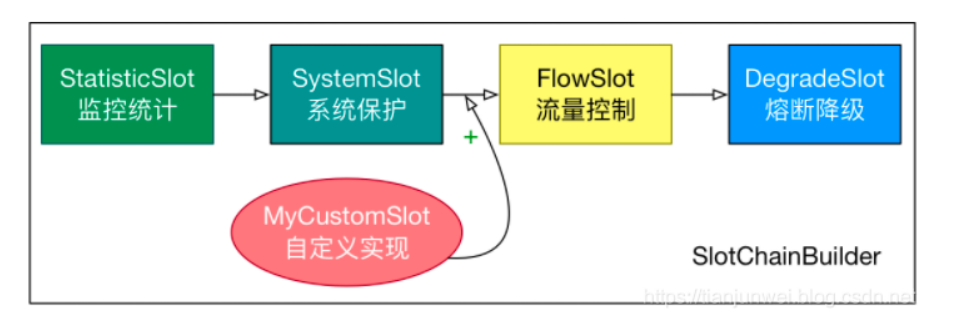
总体的框架如下:
Sentinel 将 SlotChainBuilder 作为 SPI 接口进行扩展,使得 Slot Chain 具备了扩展的能力。您可以自行加入自定义的 slot 并编排 slot 间的顺序,从而可以给 Sentinel 添加自定义的功能。
RuleManager 规则管理器 每个 Slot 插槽背后都对应着一个 RuleManager 的实现类,简单理解就是每个 Slot 有一套规则,规则验证处理由对应的 RuleManager 来进行处理。
流量控制:FlowSolt 对应 FlowRuleManager
降级控制:DegradeSlot 对应 DegradeRuleManager
权限控制:AuthoritySlot 对应 AuthorityRuleManager
系统规则控制: SystemSlot 对应 SystemRuleManager
降级控制实现原理
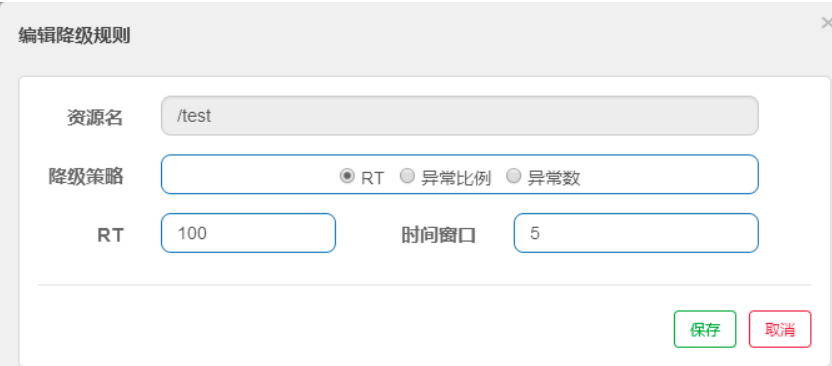
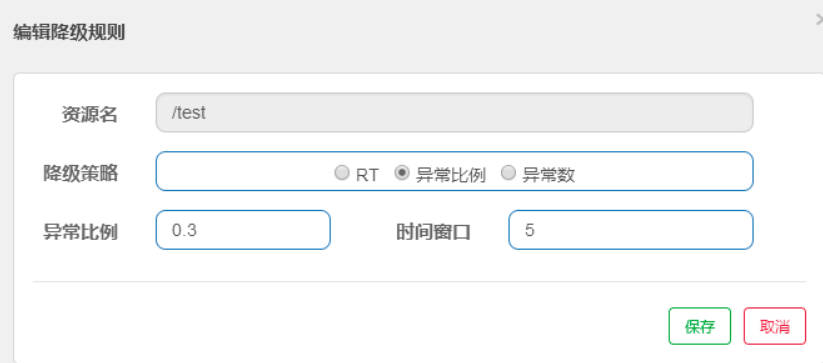
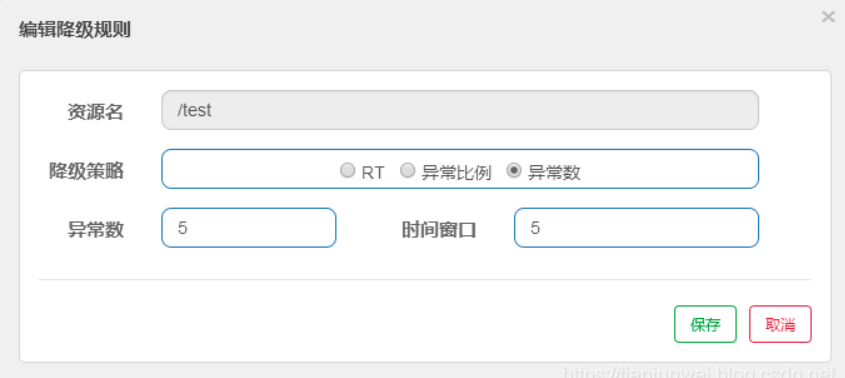
新增资源配置降级规则,目前对于降级策有如下三种:
RT:平均响应时间 (DEGRADE_GRADE_RT):当 1s 内持续进入 5 个请求,对应时刻的平均响应时间(秒级)均超过阈值(count,以 ms 为单位),那么在接下的时间窗口(DegradeRule 中的 timeWindow,以 s 为单位)之内,对这个方法的调用都会自动地熔断(抛出 DegradeException)。注意 Sentinel 默认统计的 RT 上限是 4900 ms,超出此阈值的都会算作 4900 ms,若需要变更此上限可以通过启动配置项 -Dcsp.sentinel.statistic.max.rt=xxx 来配置。
异常比例:当资源的每秒请求量 >= 5,并且每秒异常总数占通过量的比值超过阈值(DegradeRule 中的 count)之后,资源进入降级状态,即在接下的时间窗口(DegradeRule 中的 timeWindow,以 s 为单位)之内,对这个方法的调用都会自动地返回。异常比率的阈值范围是 [0.0, 1.0],代表 0% - 100%。
异常数:当资源近 1 分钟的异常数目超过阈值之后会进行熔断。注意由于统计时间窗口是分钟级别的,若 timeWindow 小于 60s,则结束熔断状态后仍可能再进入熔断状态。
限流结果信息
Blocked by Sentinel (flow limiting)
实现逻辑
在之前我们已经提及 Sentinel 是通过 slot 链来实现的,对于降级功能其提供了 DegradeSlot,实现源码如下:
public class DegradeSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot <DefaultNode> { @Override public void entry (Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable { DegradeRuleManager.checkDegrade(resourceWrapper, context, node, count); fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args); } @Override public void exit (Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) { fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args); } }
通过上面代码我们可以了解到,限流规则的实现是在 DegradeRuleManager 的checkDegrade中来处理的,限流可以-配置多个规则,依次按照规则来处理。
public static void checkDegrade (ResourceWrapper resource, Context context, DefaultNode node, int count) throws BlockException { Set<DegradeRule> rules = degradeRules.get(resource.getName()); if (rules == null ) { return ; } for (DegradeRule rule : rules) { if (!rule.passCheck(context, node, count)) { throw new DegradeException (rule.getLimitApp(), rule); } } }
在 DegradeRule 的 passCheck 方法中我们可以看到可以根据 RT、异常数和异常比例来进行熔断降级处理。
@Override public boolean passCheck (Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount, Object... args) { if (cut.get()) { return false ; } ClusterNode clusterNode = ClusterBuilderSlot.getClusterNode(this .getResource()); if (clusterNode == null ) { return true ; } if (grade == RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_RT) { double rt = clusterNode.avgRt(); if (rt < this .count) { passCount.set(0 ); return true ; } if (passCount.incrementAndGet() < rtSlowRequestAmount) { return true ; } } else if (grade == RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_RATIO) { double exception = clusterNode.exceptionQps(); double success = clusterNode.successQps(); double total = clusterNode.totalQps(); if (total < minRequestAmount) { return true ; } double realSuccess = success - exception; if (realSuccess <= 0 && exception < minRequestAmount) { return true ; } if (exception / success < count) { return true ; } } else if (grade == RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_COUNT) { double exception = clusterNode.totalException(); if (exception < count) { return true ; } } if (cut.compareAndSet(false , true )) { ResetTask resetTask = new ResetTask (this ); pool.schedule(resetTask, timeWindow, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } return false ; }
流量控制实现原理 接下来我们了解学习一下 Sentinel 是如何实现流量控制的
流量控制(flow control),其原理是监控应用流量的 QPS 或并发线程数等指标,当达到指定的阈值时对流量进行控制,以避免被瞬时的流量高峰冲垮,从而保障应用的高可用性。
FlowSlot 会根据预设的规则,结合前面 NodeSelectorSlot、ClusterNodeBuilderSlot、StatisticSlot 统计出来的实时信息进行流量控制。
限流的直接表现是在执行 Entry nodeA = SphU.entry(resourceName) 的时候抛出 FlowException 异常。FlowException 是 BlockException 的子类,您可以捕捉 BlockException 来自定义被限流之后的处理逻辑。
同一个资源可以创建多条限流规则。FlowSlot 会对该资源的所有限流规则依次遍历,直到有规则触发限流或者所有规则遍历完毕。
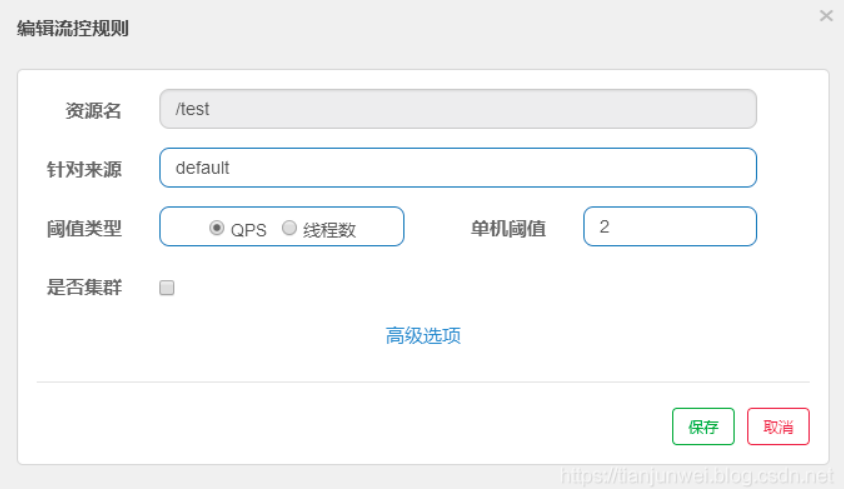
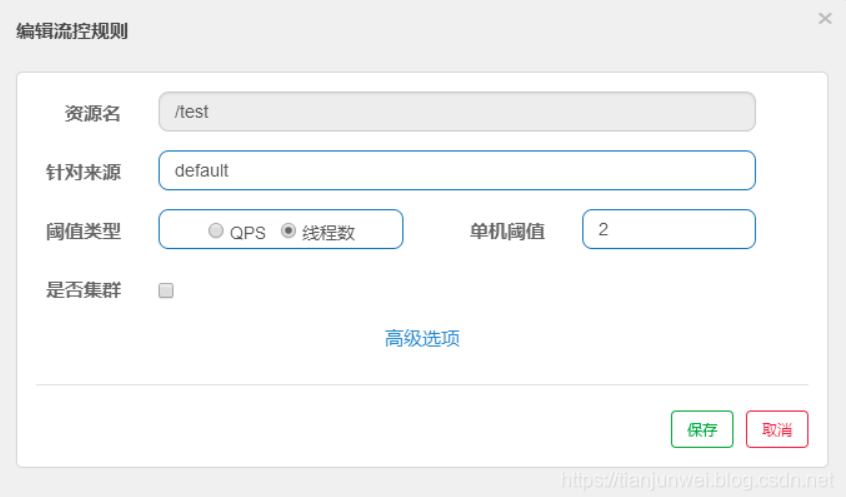
一条限流规则主要由下面几个因素组成,我们可以组合这些元素来实现不同的限流效果:
resource:资源名,即限流规则的作用对象
count: 限流阈值
grade: 限流阈值类型(QPS 或并发线程数)
limitApp: 流控针对的调用来源,若为 default 则不区分调用来源
strategy: 调用关系限流策略
controlBehavior: 流量控制效果(直接拒绝、Warm Up、匀速排队)
流控-QPS配置
流控-线程数配置
实现流程 Sentinel 提供了 FlowSlot 用来进行流量控制,流量规则的最终实现在 FlowRuleChecker 的 checkFlow 中实现的。
public class FlowSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot <DefaultNode> { private final FlowRuleChecker checker; public FlowSlot () { this (new FlowRuleChecker ()); } FlowSlot(FlowRuleChecker checker) { AssertUtil.notNull(checker, "flow checker should not be null" ); this .checker = checker; } @Override public void entry (Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable { checkFlow(resourceWrapper, context, node, count, prioritized); fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args); } void checkFlow (ResourceWrapper resource, Context context, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized) throws BlockException { checker.checkFlow(ruleProvider, resource, context, node, count, prioritized); } @Override public void exit (Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) { fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args); } private final Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>> ruleProvider = new Function <String, Collection<FlowRule>>() { @Override public Collection<FlowRule> apply (String resource) { Map<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRules = FlowRuleManager.getFlowRuleMap(); return flowRules.get(resource); } }; }
在 checkFlow 中会依次获取我们配置的流控规则,然后依次进行流控判断处理,如果被流控则抛出异常 FlowException
public void checkFlow (Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>> ruleProvider, ResourceWrapper resource, Context context, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized) throws BlockException { if (ruleProvider == null || resource == null ) { return ; } Collection<FlowRule> rules = ruleProvider.apply(resource.getName()); if (rules != null ) { for (FlowRule rule : rules) { if (!canPassCheck(rule, context, node, count, prioritized)) { throw new FlowException (rule.getLimitApp(), rule); } } } }
在 canPassCheck 中会判断是集群限流还是本地限流
public boolean canPassCheck ( FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) { String limitApp = rule.getLimitApp(); if (limitApp == null ) { return true ; } if (rule.isClusterMode()) { return passClusterCheck(rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized); } return passLocalCheck(rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized); }
如果是本地限流则获取节点信息,然后根据流控规则进行流控判断
private static boolean passLocalCheck (FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) { Node selectedNode = selectNodeByRequesterAndStrategy(rule, context, node); if (selectedNode == null ) { return true ; } return rule.getRater().canPass(selectedNode, acquireCount, prioritized); }
当 QPS 超过某个阈值的时候,则采取措施进行流量控制。流量控制的手段包括以下几种:直接拒绝、Warm Up、匀速排队。对应 FlowRule 中的 controlBehavior 字段。
直接拒绝(RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_DEFAULT)方式是默认的流量控制方式,当QPS超过任意规则的阈值后,新的请求就会被立即拒绝,拒绝方式为抛出FlowException。这种方式适用于对系统处理能力确切已知的情况下,比如通过压测确定了系统的准确水位时。具体的例子参见 FlowQpsDemo。
Warm Up(RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_WARM_UP)方式,即预热/冷启动方式。当系统长期处于低水位的情况下,当流量突然增加时,直接把系统拉升到高水位可能瞬间把系统压垮。通过”冷启动”,让通过的流量缓慢增加,在一定时间内逐渐增加到阈值上限,给冷系统一个预热的时间,避免冷系统被压垮。详细文档可以参考 流量控制 - Warm Up 文档
目前 Sentinel 对于流量控制提供了如下几种方式:
直接拒绝(DefaultController):支持抛出异常@Override public boolean canPass (Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) { int curCount = avgUsedTokens(node); if (curCount + acquireCount > count) { if (prioritized && grade == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS) { long currentTime; long waitInMs; currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis(); waitInMs = node.tryOccupyNext(currentTime, acquireCount, count); if (waitInMs < OccupyTimeoutProperty.getOccupyTimeout()) { node.addWaitingRequest(currentTime + waitInMs, acquireCount); node.addOccupiedPass(acquireCount); sleep(waitInMs); throw new PriorityWaitException (waitInMs); } } return false ; } return true ; }
匀速排队(RateLimiterController):判断等待时间,如果等待时间过长也是会限流,并且使用 Thread.sleep 如果配置不正确可能会导致线程过多。@Override public boolean canPass (Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) { if (acquireCount <= 0 ) { return true ; } if (count <= 0 ) { return false ; } long currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis(); long costTime = Math.round(1.0 * (acquireCount) / count * 1000 ); long expectedTime = costTime + latestPassedTime.get(); if (expectedTime <= currentTime) { latestPassedTime.set(currentTime); return true ; } else { long waitTime = costTime + latestPassedTime.get() - TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis(); if (waitTime > maxQueueingTimeMs) { return false ; } else { long oldTime = latestPassedTime.addAndGet(costTime); try { waitTime = oldTime - TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis(); if (waitTime > maxQueueingTimeMs) { latestPassedTime.addAndGet(-costTime); return false ; } if (waitTime > 0 ) { Thread.sleep(waitTime); } return true ; } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } } return false ; }
Warm Up(WarmUpController 和 WarmUpRateLimiterController):预热启动@Override public boolean canPass (Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) { long passQps = (long ) node.passQps(); long previousQps = (long ) node.previousPassQps(); syncToken(previousQps); long restToken = storedTokens.get(); if (restToken >= warningToken) { long aboveToken = restToken - warningToken; double warningQps = Math.nextUp(1.0 / (aboveToken * slope + 1.0 / count)); if (passQps + acquireCount <= warningQps) { return true ; } } else { if (passQps + acquireCount <= count) { return true ; } } return false ; }